Kicking off with Understanding GDPR Compliance, this topic delves into the essential aspects of GDPR and how organizations can ensure compliance while protecting data. From the basic principles to advanced tools and technologies, this guide has got you covered.
Overview of GDPR Compliance
GDPR, which stands for General Data Protection Regulation, is a set of regulations designed to protect the personal data of individuals within the European Union (EU). It aims to give control back to individuals over their personal data and standardize data protection laws across EU member states.
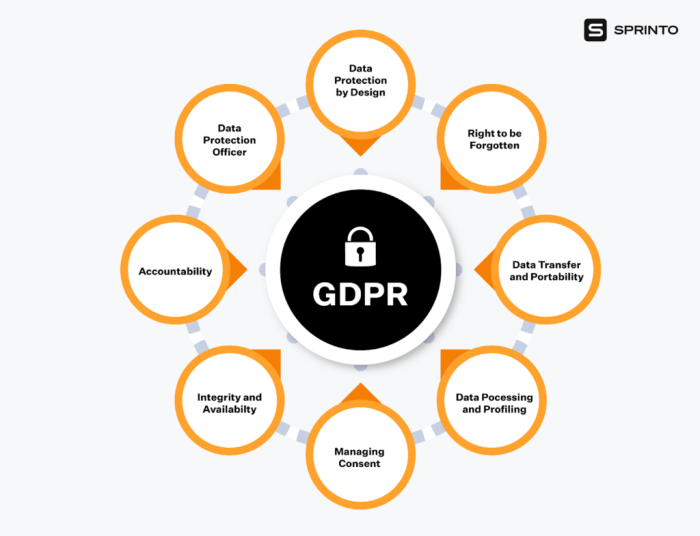
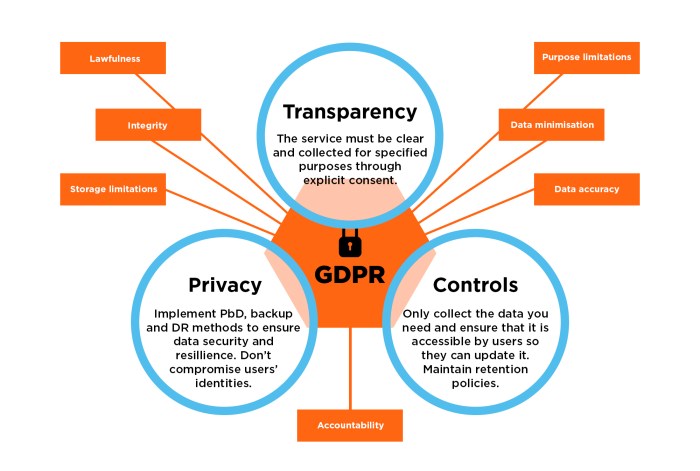
Key Principles of GDPR Compliance
- Transparency: Organizations must be clear about how they collect, process, and store personal data.
- Lawfulness, Fairness, and Purpose Limitation: Data processing must have a lawful basis, be done fairly, and be used only for specified purposes.
- Data Minimization: Collect only the data necessary for the intended purpose.
- Accuracy: Ensure data is accurate and up-to-date.
- Storage Limitation: Personal data should not be kept longer than necessary.
- Integrity and Confidentiality: Implement security measures to protect personal data.
Scope of GDPR and Compliance Requirements
The GDPR applies to organizations that process personal data of individuals residing in the EU, regardless of where the organization is located. This includes businesses, non-profits, government agencies, and any entity that handles personal data.
Examples of Data Covered under GDPR
- Names
- Addresses
- Email addresses
- IP addresses
- Biometric data
Understanding GDPR Requirements: Understanding GDPR Compliance
When it comes to GDPR compliance, there are several key requirements that businesses need to meet in order to protect the personal data of individuals.
Role of Data Controllers and Data Processors
Data controllers are responsible for determining the purposes and means of processing personal data, while data processors act on behalf of the controller. Both parties must comply with GDPR regulations to ensure data protection.
Conditions for Consent under GDPR
Consent under GDPR must be freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous. Individuals must have the option to withdraw their consent at any time. It’s essential for businesses to obtain clear consent before processing personal data.
Examples of GDPR Compliance Measures
– Implementing strong data encryption measures to protect sensitive information.
– Conducting regular data protection impact assessments to identify and mitigate risks.
– Providing transparency to individuals about how their data is being used and stored.
– Training employees on data protection practices to ensure compliance with GDPR regulations.
Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)
Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) is a process that helps organizations identify and minimize the data protection risks of a project. It is an essential part of GDPR compliance as it ensures that data protection is considered at the early stages of any new project or process involving personal data.
Steps in Conducting a DPIA
- Identify the need for a DPIA: Determine if the processing of personal data poses a high risk to individuals’ rights and freedoms.
- Describe the processing: Document the nature, scope, context, and purposes of the processing.
- Assess necessity and proportionality: Evaluate the necessity of the processing activities and ensure they are proportionate to the intended purpose.
- Identify and assess risks: Identify potential data protection risks and assess their likelihood and severity.
- Propose measures to address risks: Develop measures to mitigate or eliminate the identified data protection risks.
- Review and consult: Review the DPIA process and outcomes and consult with relevant stakeholders.
- Integrate measures: Integrate the measures into the project plan and monitor their effectiveness.
Importance of DPIA in GDPR Compliance
DPIA helps in identifying and minimizing data protection risks by ensuring that organizations assess the impact of their data processing activities on individuals’ privacy. By conducting a DPIA, organizations can proactively address potential risks and implement measures to protect personal data effectively.
Examples of Scenarios Requiring DPIA
Launching a new product that involves extensive data processing, such as a health tracking app or a biometric access system.
Implementing new technologies like facial recognition software or IoT devices that collect personal data.
Processing sensitive data on a large scale, such as genetic information or criminal records.
GDPR Compliance Tools and Technologies
In order to meet the requirements of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), companies can utilize various tools and technologies to ensure compliance and protect the personal data of individuals.
Data Mapping and Inventory Tools
- Data mapping tools help organizations identify and document all personal data they collect, store, and process.
- Inventory tools assist in maintaining a record of data processing activities, data flows, and data storage locations.
- Examples of such tools include OneTrust, TrustArc, and Collibra.
Consent Management Platforms (CMPs)
- CMPs help companies obtain, manage, and document user consent for data processing activities.
- These platforms also provide mechanisms for users to easily withdraw their consent if needed.
- Popular CMPs include Quantcast Choice, TrustArc Consent Manager, and Cookiebot.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) Solutions
- IAM solutions ensure that only authorized individuals have access to personal data.
- These tools help manage user identities, permissions, and access controls within an organization.
- Examples of IAM solutions are Okta, Microsoft Azure Active Directory, and Ping Identity.
Encryption and Anonymization Technologies, Understanding GDPR Compliance
- Encryption helps protect personal data by converting it into a secure format that can only be accessed with the appropriate decryption key.
- Anonymization techniques remove identifying information from data, making it impossible to link back to an individual.
- Companies can use encryption tools like VeraCrypt, BitLocker, and OpenSSL, along with anonymization software such as ARX Data Anonymization Tool.
Innovative Technologies for GDPR Compliance
- Some companies are leveraging blockchain technology for secure and transparent data management in compliance with GDPR.
- AI-powered tools are being used for data classification, monitoring, and incident response to enhance GDPR compliance efforts.
- Companies like IBM, Oracle, and SAP are developing advanced technologies to help organizations meet GDPR requirements effectively.