Kicking off with Using Heatmaps for UX, this topic delves into the world of data visualization to improve user experience. From analyzing user behavior to implementing strategies for optimization, heatmaps offer a unique insight into understanding and enhancing UX design.
Introduction to Heatmaps
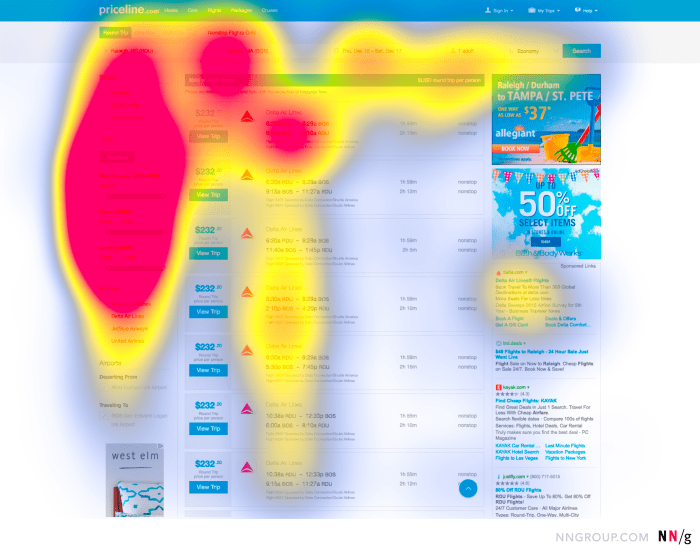
Heatmaps are visual representations of data that show the intensity of user interactions on a website or app. In the context of UX design, heatmaps are valuable tools for analyzing user behavior and optimizing the design for better user experience.
Types of Heatmaps
- Click Heatmaps: Show where users click the most on a page, helping to identify popular or ignored areas.
- Scroll Heatmaps: Display how far users scroll down a page, indicating where content is most engaging or where users lose interest.
- Mouse Movement Heatmaps: Track the movement of the mouse cursor, highlighting patterns and areas of interest.
- Attention Heatmaps: Combine click, scroll, and mouse movement data to provide a comprehensive view of user interactions.
Benefits of Using Heatmaps for UX Research and Design
- Visual Insights: Heatmaps offer a visual way to understand user behavior quickly and easily.
- Data-Driven Decisions: By analyzing heatmaps, designers can make informed decisions based on user interactions.
- Identify Pain Points: Heatmaps help identify areas of a website that may need improvement or optimization.
- Optimize User Experience: With insights from heatmaps, designers can enhance the user experience and improve website performance.
Types of Heatmaps
When it comes to analyzing user behavior on a website, different types of heatmaps play a crucial role in providing valuable insights. Click maps, scroll maps, and move maps each offer unique perspectives on how users interact with a website.
Click Maps
Click maps track where users click on a webpage, showing hotspots of user activity. By analyzing click maps, UX designers can understand which elements are attracting the most attention and which areas may be overlooked. For example, click maps can help identify popular navigation links, buttons, or calls to action that may need to be optimized for better user engagement.
Scroll Maps
Scroll maps visualize how far users scroll down a webpage, indicating where users typically lose interest or abandon the page. This type of heatmap can highlight the most engaging sections of a webpage and identify areas that may need to be restructured for better user retention. For instance, scroll maps can reveal if important content is buried too deep on a page, prompting designers to make adjustments for better visibility.
Move Maps
Move maps track the movement of the cursor as users navigate a webpage, showing the flow of attention and interaction. By analyzing move maps, designers can gain insights into how users explore a page and where they may encounter confusion or distractions. For instance, move maps can reveal if users are struggling to find specific information or navigate through complex menus, leading to improvements in the overall user experience.
Overall, each type of heatmap offers valuable insights into user behavior and interaction, helping UX designers make informed decisions to optimize website usability and engagement.
Implementing Heatmaps: Using Heatmaps For UX
Implementing heatmaps on a website or application is crucial for understanding user behavior and improving overall user experience. By setting up heatmap tracking tools and accurately interpreting the data, businesses can make informed decisions to enhance their digital platforms.
Setting Up Heatmap Tracking Tools
- Choose a reliable heatmap tool that aligns with your specific goals and budget.
- Install the heatmap tracking code on all relevant pages of your website or application.
- Set up specific parameters and filters to track user interactions based on your objectives.
- Regularly monitor and analyze heatmap data to identify patterns and trends.
Interpreting Heatmap Data
- Focus on hotspots or areas with the most user activity to prioritize improvements.
- Pay attention to cold spots or areas with little to no interaction to identify potential issues.
- Consider user behavior patterns such as scrolling, clicking, and mouse movement to optimize layout and content placement.
- Use A/B testing to validate hypotheses and make data-driven decisions for enhancing UX.
Heatmaps for User Engagement
When it comes to understanding user engagement levels, heatmaps can be a valuable tool. By visually representing user interactions on a website or app, heatmaps provide insights into where users are most and least engaged.
Let’s dive into how heatmaps can help identify areas of high and low user interest and discuss strategies for improving user engagement based on heatmap analysis.
Identifying Areas of Interest
Heatmaps can pinpoint specific areas of a webpage or app that receive the most user attention. By analyzing where users click, scroll, or hover the most, you can identify popular sections and features that capture user interest.
Improving User Engagement Strategies
- Use heatmaps to optimize the placement of important content or CTAs based on user interaction data.
- Identify and fix usability issues in areas with low user engagement to enhance the overall user experience.
- Analyze scroll depth to determine if users are engaging with your content or leaving the page prematurely.
- Experiment with different layouts and designs in high-traffic areas to maximize user engagement.
Heatmaps for Conversion Rate Optimization
When it comes to optimizing conversion rates, heatmaps play a crucial role in providing valuable insights into user behavior on a website. By visually representing user interactions, heatmaps help identify areas of improvement to enhance the conversion process.
Pinpointing Conversion Barriers
Heatmaps can pinpoint conversion barriers on a website by highlighting areas where users are dropping off or encountering obstacles. Whether it’s a confusing layout, unclear call-to-action buttons, or lengthy forms, heatmaps can reveal the pain points that hinder conversions.
Strategies for A/B Testing
- Utilize heatmaps to identify underperforming areas on the website that may be impacting conversion rates.
- Run A/B tests to compare different versions of the webpage and analyze which one performs better in terms of conversions.
- Implement changes based on heatmap findings, such as adjusting the placement of buttons, simplifying the checkout process, or improving the overall user experience.
- Continuously monitor and analyze heatmap data to track the effectiveness of implemented changes and make further optimizations.